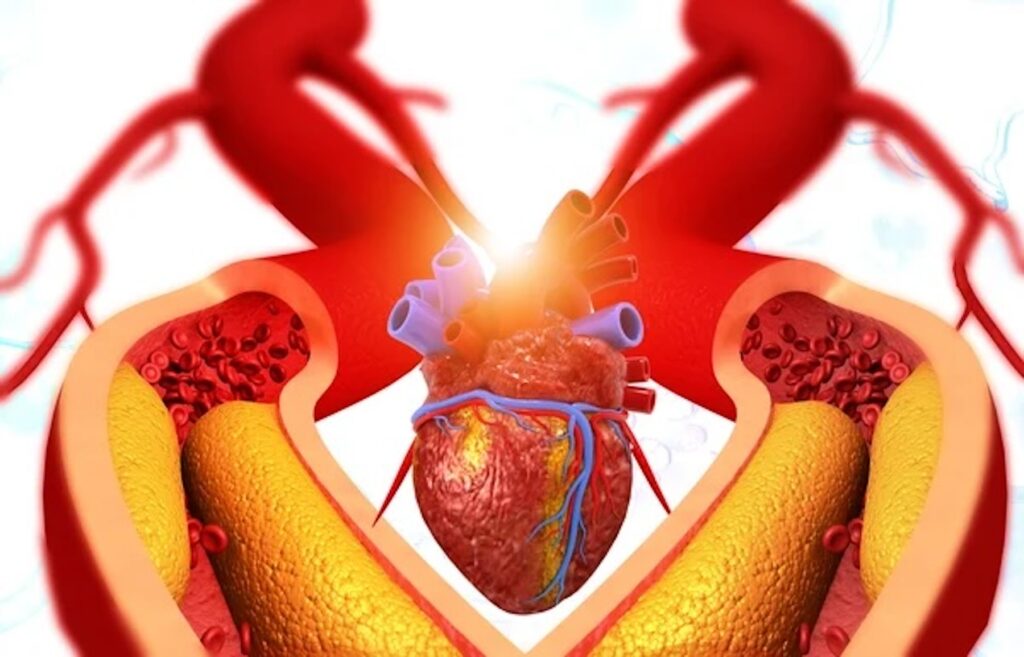
Do you often feel tired or out of breath, even at rest? Do your arms and legs ache or swell with minimal exercise? If so, this could be a sign that the arteries responsible for circulating blood from the heart to the body may be clogged. But what causes clogged arteries, and how do you prevent them?
Ignoring the signs of clogged arteries can lead to serious health events, such as stroke, difficulty breathing, and even death. To protect your health, start by learning the common conditions associated with clogged arteries. Cardiovascular Institute of the South can help you understand what causes clogged arteries, related issues, and ways to manage or prevent them.
What Causes Clogged Arteries?
Atherosclerosis is the medical term for arteries that have become thick, stiff, and narrowed over time due to a buildup of cholesterol and fatty deposits. This buildup is also referred to as plaque. Plaque buildup restricts blood flow throughout the body, increasing the risk of health issues including:
- Blood clots
- Angina (chest pain or pressure)
- Numbness or weakness in the arms or legs
- Arrhythmia
Many people think of clogged arteries as a problem that occurs only in the heart. However, atherosclerosis can affect arteries throughout the body, including the brain, arms, and legs. Here are three conditions that can develop due to atherosclerosis.
1. Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked. This buildup reduces blood flow to the heart and can become life-threatening over time.
Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue with exertion
- Weakness or dizziness
- Heart palpitations
Understanding what causes clogged arteries is essential to managing coronary artery disease effectively. Addressing risk factors like high cholesterol can help prevent the progression of this disease.
2. Carotid Artery Disease (CAD)
The carotid arteries are the major arteries in your neck that supply blood to the brain, face, and scalp. Carotid artery disease occurs when these arteries become hardened, blocked, or narrowed by atherosclerosis or plaque buildup.
Over time, these clogged arteries reduce the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the brain. If a piece of plaque breaks off from the artery walls, it can travel to the smaller arteries in the brain and cause a blockage, leading to a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke.
3. Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Peripheral arterial disease is a medical condition caused by fatty deposit buildup in the arteries that supply blood to the arms and legs, leading to inadequate blood flow. This can also be caused by:
- Blood vessel inflammation
- Physical injury
- Abnormal anatomy structures near vessels
- Or elevated risk factors unique to an individual’s lifestyle
As an atherosclerosis-driven disease, PAD carries significant health risks if left untreated. These risks include:
- Pain during movement
- Potential limb loss
- Stroke
- Or heart attack
PAD can be mistaken for typical signs of aging due to its subtle development. However, this disease affects over 8 million Americans aged 40 and older. Because of its subtle or nonexistent symptoms, PAD often goes undetected until it has progressed significantly. Knowing what to look for may help you identify these conditions so that you can seek care sooner.
The following two complications can occur in the advanced stages of PAD.
Claudication
This common yet debilitating condition causes leg pain during physical activity. In its most severe cases, this discomfort can persist during rest periods and may come with additional symptoms in the lower body, such as:
- Pain or numbness
- Weakness
- Cold sensations
- Hair Loss
Critical Limb Ischemia (CLI)
CLI is a severe form of PAD that can cause wounds and infections in the lower body to worsen. This can result in gangrene or tissue death. Without treatment, these complications could lead to amputation. However, with timely and effective treatment, amputation can be avoided. This is why those with CLI need to have their condition diagnosed as soon as possible.
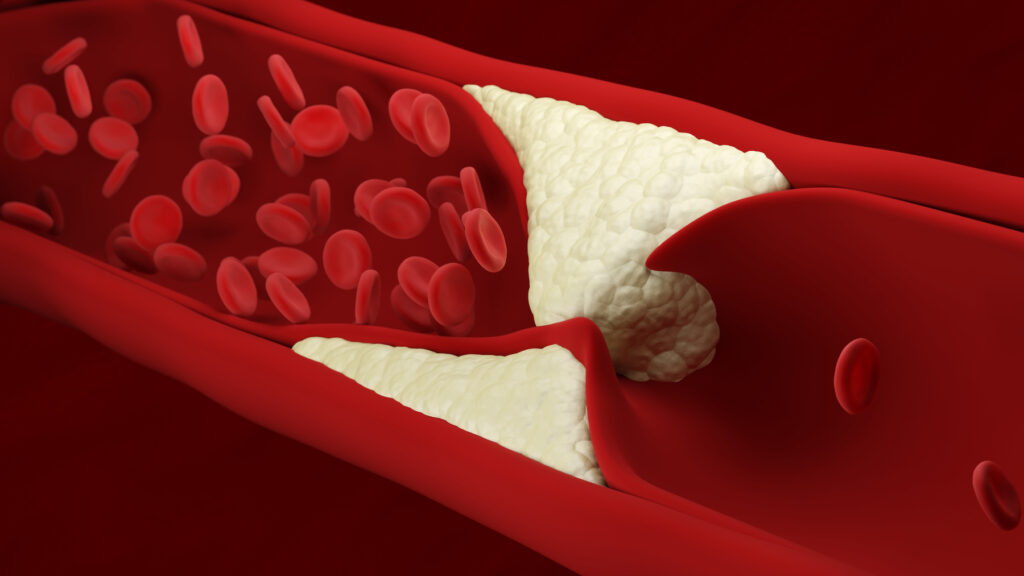
What Factors Increase Your Risk for Clogged Arteries?
In terms of what causes clogged arteries, many risk factors can weaken arteries and increase fat deposits and cholesterol. Men 45 years or older and women 55 years or older are at highest risk of developing plaque buildup.
Additionally, any of the following health concerns can increase a patient’s risk of developing atherosclerosis:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- High-fat diet, obesity, or lack of exercise
- Inflammatory diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis
- Family history
Signs of Clogged Arteries
In addition to understanding what causes clogged arteries, knowing what symptoms to look out for is essential. Because there are several conditions associated with clogged arteries, these can affect different parts and processes of the body in various ways. The following signs could indicate health issues related to clogged arteries:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue or difficulty performing physical activities
- Nausea
- Sweating
- Shortness of breath
- Vision loss
- Slurred speech
- Severe chest pain or pressure
- Heart palpitations (strong, fast, or irregular heartbeat)
Clogged arteries often affect the lower body. Symptoms in the lower extremities can include:
- Numbness or tingling in the arms or legs
- Cold sensations in the feet and legs
- Skin discoloration (pale, blueish, dry, or cracked in appearance)
- Slowed healing wounds
Additionally, you may experience pain or cramping in the following areas:
- Head
- Neck
- Jaw
- Ear lobes
- Upper back
- Arms
- Calves
- Thighs
- Hips
- Or buttocks
While this is an extensive list of symptoms, the early stages of clogged arteries may not have any noticeable symptoms. Contact Cardiovascular Institute of the South if you experience any of these symptoms, especially in combination. And, if you are not experiencing symptoms but are concerned about your cardiovascular health or have a family history of clogged arteries, make an appointment with us for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
What Are the Complications Associated With Clogged Arteries?
Leaving any health problem unaddressed and unmanaged can be dangerous for one’s wellness. This is especially true for clogged arteries.
A cardiologist can help you reduce the risks of atherosclerosis through medications or recommended lifestyle changes. However, failing to follow these directions can lead to severe health events, including heart attack or stroke — and, in the case of PAD, possible limb amputation.
When Should You Worry About Clogged Arteries?
Everyone should be mindful of what causes clogged arteries, particularly those suffering from related health conditions such as those listed above. If you suffer from any of these, contact your physician immediately.
Additionally, scheduling regular visits to your cardiologist beginning in your 20s can be essential in managing or preventing cardiovascular diseases. Don’t wait to prioritize your health!
Schedule an Appointment at Cardiovascular Institute of the South Today
If you have more questions about what causes clogged arteries, our team is here to help. Request an appointment today with one of our highly skilled cardiologists. We can discuss potential risk factors and symptoms, especially if you believe you may have atherosclerosis or an associated condition. Let our experts at Cardiovascular Institute of the South help you take the first steps toward better health today.